Built-in signal generators¶
Neuralynx raw data (nlx)¶
To define a signal source that reads raw data packets from a previously recorded Neuralynx raw data file, you would use the nlx source class and set the file option to the path where the raw data file can be found. Importantly, the raw data file should contain recorded signals from exactly 128 channels. This is a limitation of the nlxtestbench tool that will hopefully be removed in the future. All data packets in the file will be streamed, unless a maximum number of data packets has been specified that is less than the number of available data in the file (see stream options). If the cycle options is set to true, then streaming of the data in the file will restart automatically once the end of the file was reached.
Ripple signal (ripple)¶
The ripple signal is used to work with the ripple detection graph. A ripple is characterize by its frequency, its mean amplitude, its duration, its zero interval between two ripples.
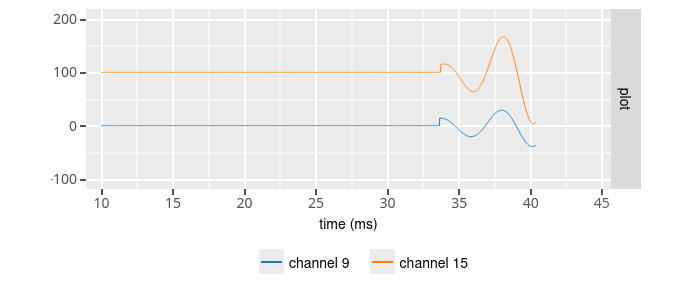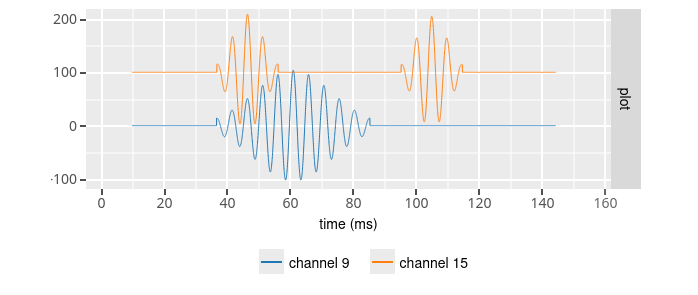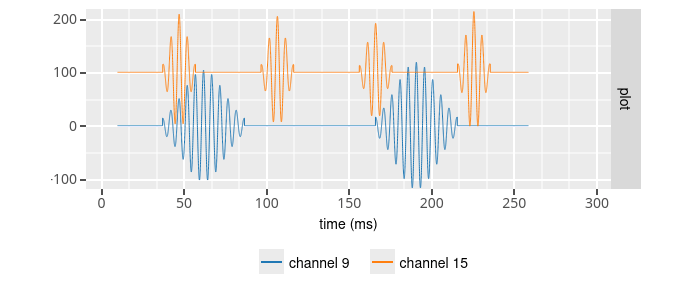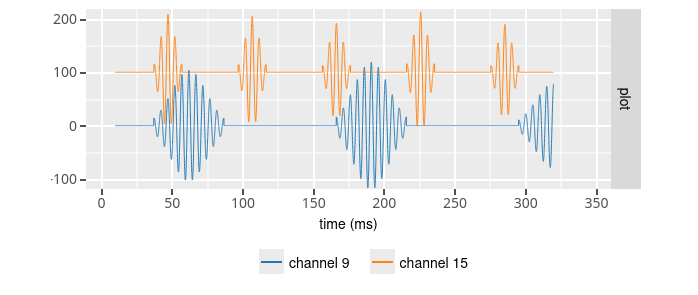
This configuration create a
ripple wave (fs = 32000.0 Hz, offset = 0.0 uV, noise stdev = 0.0 uV, number of channels = 128, convert byte order = 1,
For all channels : mean ripple amplitude = 100.0 uV, ripple frequency = 200.0 Hz, ripple duration = 100 ms, zero signal interval = 50 ms
Except for channel 9 : ripple duration = 50 ms, zero signal interval = 80 ms
Except for channel 15 : ripple duration = 20 ms, zero signal interval = 40 ms )
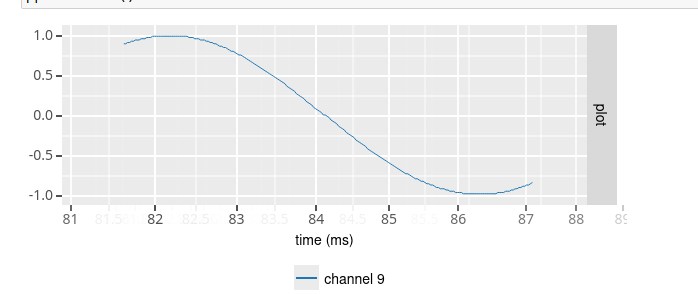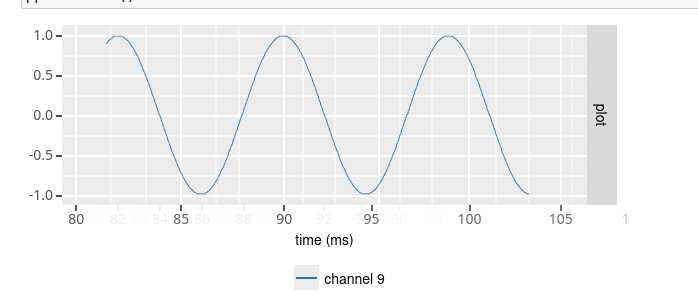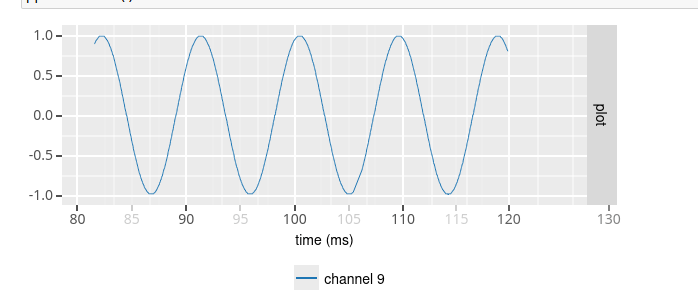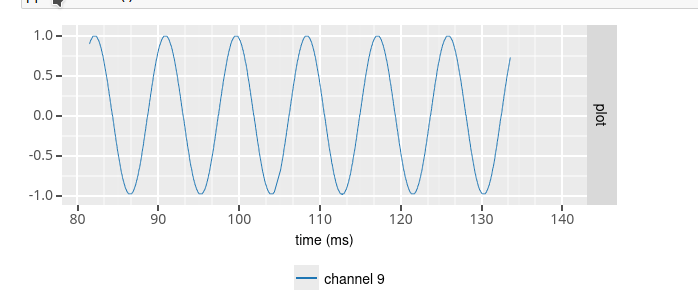
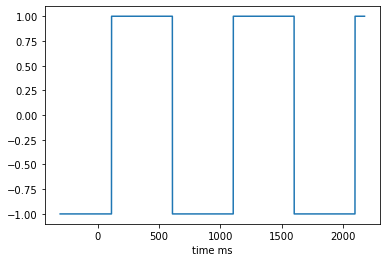
Periodic signal (sine / square)¶
To define a source that generates a periodic signal, you would use the sine and square source class. You then specify the offset (in microVolt), amplitude (in microVolt) and frequency (in Hz) of the sine/square wave. In addition, you can specify a sampling rate other than 32 kHz using the sampling_rate option. And finally, noise may be added to the signal by setting the noise_stdev option to the standard deviation of a Gaussian noise distribution (in microVolt).
White noise (noise)¶
To define a source that generates white noise, you would use the noise class. You can specify both the mean and standard deviation (stdev) of the Gaussian noise distribution (in microVolt). You can specify a sampling rate other than 32 kHz using the sampling_rate option.